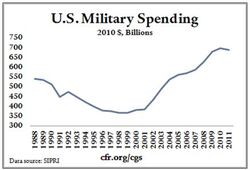
-
US superpower since 1990's
Vocabulary
Cold War
The USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
A collapse
Bipolar / unipolar / multipolar world
Unilateralism: doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action.
Multilateralism: multiple countries working in concert on a given issue
New world order: George H. W. Bush used the term to try to define the nature of the post Cold War era, and the spirit of great power cooperation that they hoped might materialize.
Enlargement: The Doctrine of Enlargement asked for
- A free competition in global trade,
- promoting democracy with minimum intervention in foreign political affairs
- while America to be remaining as the global leader.
NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization, intergovernmental military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed on 4 April 1949. The organization constitutes a system of collective defense whereby its member states agree to mutual defense in response to an attack by any external party.
Hyper power: used to describe the United States' position as the lone power since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 (during the Cold War, USA and USSR were called Superpower)
Soft power: ability to attract and co-opt rather than coerce, use force or give money as a means of persuasion.
Hard Power: use of military and economic means to influence the behavior or interests of other political bodies.
Islamic fundamentalism: group of religious ideologies seen as advocating a return to the fundamentals of Islam: the Quran and the Sunnah.
Taliban: Islamic fundamentalist political movement which spread from Pakistan into Afghanistan and formed a government, ruling as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan from September 1996 until December 2001.
Al-Qaeda: global militant Islamist organization founded by Osama bin Laden in Pakistan. It operates as a network comprising both a multinational army and a radical Sunni Muslim movement calling for global Jihad. It has been designated as a terrorist organization by the United Nations Security Council.
Suicide hijackers: men who commit suicide as a weapon and terrorist tactic.
The War on Terror (also known as the Global War on Terrorism) is a term commonly applied to an international military campaign which started as a result of the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States. This resulted in an international military campaign to eliminate al-Qaeda and other militant organizations.
Rogue states: controversial term applied by some international theorists to states they consider threatening to the world's peace. The term is used most by the United States, though the US State Department officially quit using the term in 2000.
Guantanamo: controversial United States military prison located within Guantanamo Bay Naval Base (Cuba) that was established in January 2002 in order to detain extraordinarily dangerous prisoners, to interrogate prisoners in an optimal setting, and to prosecute prisoners for war crimes.
Anti-Americanism or anti-American sentiment: refers to opposition or hostility to the policies, culture, society, economics, international, or superpower role of the United States.
Neo-conservatism : A belief deriving from religious conviction that the human condition is defined as a choice between good and evil and that the true measure of political character is to be found in the willingness by the former (themselves) to confront the latter. AND An assertion that the fundamental determinant of the relationship between states rests on military power and the willingness to use it. AND A primary focus on the Middle East and global Islam as the principal theater for American overseas interests.
Smart Power: combination of hard power and soft power strategies.
New Beginning: name of a speech delivered by United States President Barack Obama on 4 June 2009, at Cairo University in Egypt. The speech honors a promise Obama made during his presidential campaign to give a major address to Muslims from a Muslim capital during his first few months as president.
Events
- 1989: Defeat and withdrawal (retrait) from Afghanistan
- November 9th, 1989: Fall of the Berlin Wall
- September 12th, 1990: Reunification of Germany
- 1991: Collapse of the USSR. USSR was destabilized by a vast economic crisis, its state is undermined by mafias and its world influence got weaker (-40% of its lands)
- August 1990: Iraqi invasion of Kuwait
- January 1991: Gulf War, codenamed Operation Desert Storm (17 January 1991 – 28 February 1991), a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.
- January 28th, 1992 : State of the Union Adress, George Bush
- 1986-1994: Uruguay Round, The Round led to the creation of the World Trade Organization. The broad mandate of the Round had been to extend GATT trade rules to areas previously exempted as too difficult to liberalize (agriculture, textiles) and increasingly important new areas previously not included (trade in services, intellectual property, investment policy trade distortions).
- 1993: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), A forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
- 1993: Unified Task Force (UNITAF) was an American-led, United Nations-sanctioned multinational force which operated in Somalia. A United States initiative (code-named Operation Restore Hope), UNITAF was charged to create a protected environment for conducting humanitarian operations in the southern half of the country.
- September 13th 1993: The Oslo I Accord, officially called the Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements or Declaration of Principles (DOP), was an attempt to set up a framework that would lead to the resolution of the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict. It was the first face-to-face agreement between the government of Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- 1994: North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), An agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America.
- 1994: NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- November-December 1995: Dayton-Paris Agreement: peace agreement reached near Dayton, in November, and formally signed in Paris on December 1995. These accords put an end to the 3 and a half-year long Bosnian War, one of the armed conflicts in the former Socialist Federative Republic of Yugoslavia.
- 1997: The United States signed but did not ratify the Kyoto Protocol which is an international treaty that sets binding obligations on industrialised countries to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases.
- 1998: The United Stated refused to join the International Criminal Court which is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression.
- 1998: bombings of Afghanistan and Sudan (codenamed Operation Infinite Reach by the United States), American cruise missile strikes on terrorist bases in Afghanistan and a pharmaceutical factory in Sudan. The attack was in retaliation for the bombings of American embassies in Kenya and Tanzania.
- December 1998: bombing of Iraq (code-named Operation Desert Fox) by the United States and United Kingdom. The contemporaneous justification for the strikes was Iraq's failure to comply with United Nations Security Council resolutions as well as their interference with United Nations Special Commission inspectors.
- 1999: The United Stated refused to ratify the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) which is a multilateral treaty by which states agree to ban all nuclear explosions in all environments, for military or civilian purposes.
- 1999: Kosovo war
- 1999: Poland, Hungary and Czech Republic join NATO
- September 11th 2001: 9/11 attacks
- October 7th 2001: the U.S. government launched military operations in Afghanistan with the agreement of UN.
- March 20th 2003: invasion of Iraq starting on by an invasion force led by the United States without the agreement of UN.
- 2007: In light of 9/11 and the war in Iraq, the Bush administration was criticized for placing too much emphasis on a hard power strategy. To counter this hard power strategy, the Center for Strategic and International Studies released the "Commission on Smart Power".
-2009: The Center for Strategic and International Studies, released a second report, "Investing in a New Multilateralism", to address the concept of smart power in international releases.
- 2009: Under the Obama administration, smart power became a core principle of his foreign policy strategy. It was popularized by Hillary Clinton.
- 2011: Obama's "2011 May Speech on the Middle East and North Africa" called for a smart power strategy, incorporating development, in addition to defense and diplomacy, as the third pillar of his foreign policy doctrine.
- 2011: Libyan War
- 2011: Bin Laden’s death
Oral 1 : To what extent are the USA at a turning point with Obama's policy ?
Barack Obama's speech delivered in Cairo, June 4 2009. (video here)
I am honoured to be in the timeless city of Cairo, and to be hosted by two remarkable institutions. For over a thousand years, al-Azhar has stood as a beacon of Islamic learning, and for over a century, Cairo University has been a source of Egypt's advancement. Together, you represent the harmony between tradition and progress. I am grateful for your hospitality, and the hospitality of the people of Egypt. I am also proud to carry with me the goodwill of the American people, and a greeting of peace from Muslim communities in my country: assalaamu alaykum.
We meet at a time of tension between the United States and Muslims around the world – tension rooted in historical forces that go beyond any current policy debate. The relationship between Islam and the west includes centuries of co-existence and co-operation, but also conflict and religious wars. More recently, tension has been fed by colonialism that denied rights and opportunities to many Muslims, and a cold war in which Muslim-majority countries were too often treated as proxies without regard to their own aspirations. Moreover, the sweeping change brought by modernity and globalisation led many Muslims to view the west as hostile to the traditions of Islam.
Violent extremists have exploited these tensions in a small but potent minority of Muslims. The attacks of September 11 2001 and the continued efforts of these extremists to engage in violence against civilians has led some in my country to view Islam as inevitably hostile not only to America and western countries, but also to human rights. This has bred more fear and mistrust.
So long as our relationship is defined by our differences, we will empower those who sow hatred rather than peace, and who promote conflict rather than the co-operation that can help all of our people achieve justice and prosperity. This cycle of suspicion and discord must end.
I have come here to seek a new beginning between the United States and Muslims around the world; one based upon mutual interest and mutual respect; and one based upon the truth that America and Islam are not exclusive, and need not be in competition. Instead, they overlap, and share common principles – principles of justice and progress; tolerance and the dignity of all human beings.
I do so recognising that change cannot happen overnight. No single speech can eradicate years of mistrust, nor can I answer in the time that I have all the complex questions that brought us to this point. But I am convinced that in order to move forward, we must say openly the things we hold in our hearts, and that too often are said only behind closed doors. There must be a sustained effort to listen to each other; to learn from each other; to respect one another; and to seek common ground. As the Holy Koran tells us: "Be conscious of God and speak always the truth." That is what I will try to do – to speak the truth as best I can, humbled by the task before us, and firm in my belief that the interests we share as human beings are far more powerful than the forces that drive us apart.
 Tags : usa, since, 1991
Tags : usa, since, 1991
-
Commentaires